Lakehead University Molecular Archaeochemistry and Residue Services
Molecular Services
LUMARS provides molecular services for the characterization and identification of a large range of molecules including carbohydrates, nucleic acids, amino acids, hydrocarbons, lipids, terpenes, terpenoids, fatty acids, alkaloids, fats, phospholipids, steroids, and waxes, aromatics and inorganic compounds. These molecules may be identified as biomarkers for identification or as markers for preservation. This service is specific to the molecule of interest but can be performed on unknown substances for characterization.

Archaeochemistry Services
There are many objects or substances other than residues that can be found in the archaeological record. The archaeological chemistry and material analysis service provides a range of analyses to identify the material composition of these archaeological remains. These analyses can include elemental analysis, biochemical analysis, histological analysis, chemical analysis and microscopic analysis.
Residue Services
Archaeological, organic, inorganic and trace residue analysis can be applied to any archaeological material that is found on the surface of another. Archaeological residues can include cave art pigment, cooking residues, ceramic residue, lithic residues, food processing residues, blood residues, brewing residue, processing residues, coprolites, soil pits, caches, functional areas, paints, poisons and chemical traces.
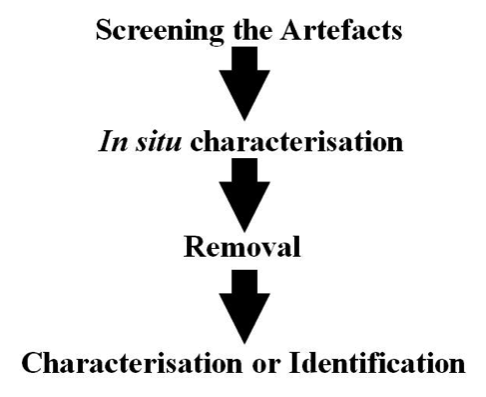
Residue analysis performed by LUMARS follows four steps and each of these steps can be performed as a separate service. It begins with screening the artefacts for the presence of a residue. While the residue is still on the artifact (in situ) it can be characterized, this may lead to identification but is performed non-destructively which is a preferred service by some Museums. The residue is then removed depending on the findings of the in situcharacterization. At this stage some researchers request the removed residue to be sent to another facility for services that LUMARS does not provide (eg. AMS dating). The final step is final characterization, identification where possible and interpretation. There are many methods employed in this final stage that varies the costs for analysis. These various methods can be requested as a separate service or LUMARS will consult with the contributor for the scope of characterization and identification. For example some contributors request GC-MS of cooking residue on ceramic material or GC-MS on hafting residue on lithics as a single service.